Table of Contents
Introduction to Keratosis Pilaris
Keratosis Pilaris, often referred to as “chicken skin,” is a common yet harmless skin condition characterized by small, hard bumps on the skin.
These bumps, which resemble goosebumps, are typically found on the upper arms, thighs, cheeks, and buttocks. Although it is not a serious medical condition, keratosis pilaris can be a cosmetic concern for many people.
This article explores the nature, causes, symptoms, and treatment options for keratosis pilaris.
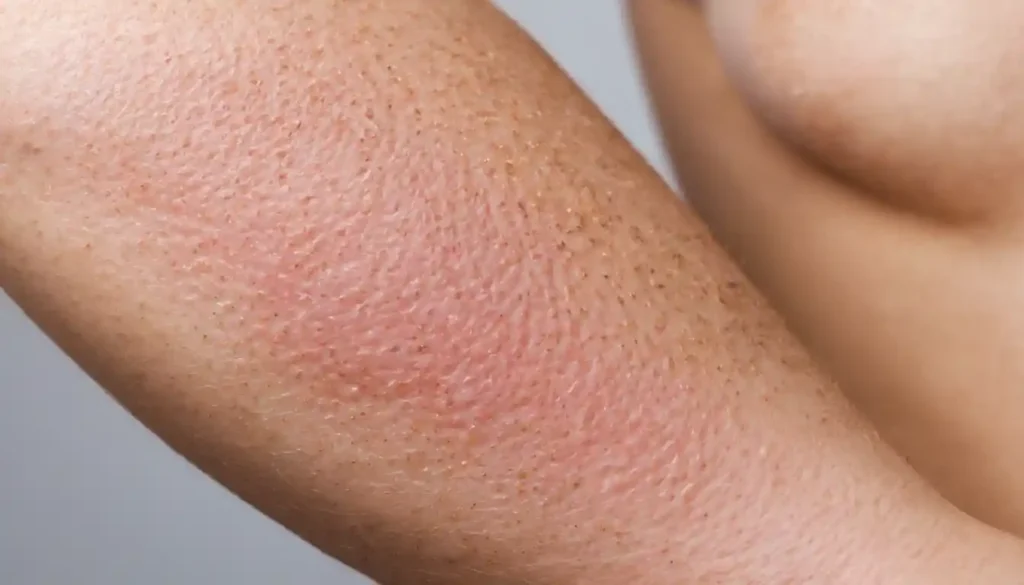
What is Keratosis Pilaris?
An Overview
Keratosis pilaris is a benign dermatological condition that affects a significant portion of the population. It results from the buildup of keratin—a protective skin protein—in hair follicles. This buildup forms small plugs that lead to the characteristic rough bumps on the skin.
Understanding the Nature of Keratosis Pilaris
The condition is often more prevalent during childhood and adolescence but can persist into adulthood. While it does not cause any harm or health issues, it can be aesthetically displeasing and sometimes lead to dry or itchy skin.
Causes of Keratosis Pilaris
The Role of Keratin in Keratosis Pilaris
Keratin plays a vital role in protecting the skin from infections and other harmful elements. However, in keratosis pilaris, excess keratin forms a plug that blocks hair follicles, leading to the formation of bumps.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Keratosis pilaris is believed to have a genetic component, as it often runs in families. Environmental factors such as dry weather can exacerbate the condition by further drying out the skin.
Risk Factors That Contribute to the Development of Keratosis Pilaris
- Genetics: A family history of keratosis pilaris increases the likelihood of developing the condition.
- Dry Skin: Individuals with naturally dry skin are more prone to experiencing symptoms.
- Other Skin Conditions: People with eczema or atopic dermatitis are at higher risk.
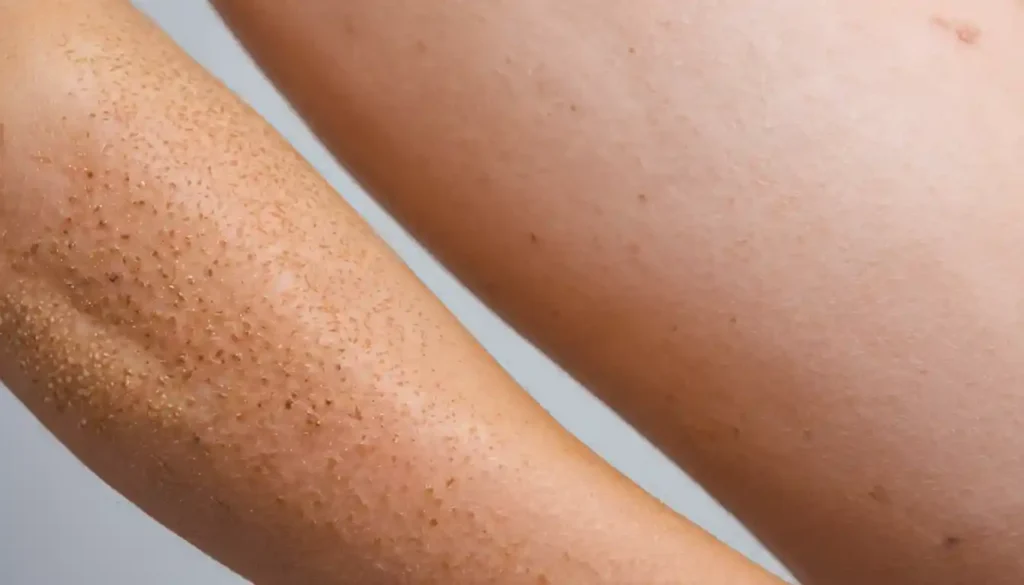

Symptoms of Keratosis Pilaris
Common Signs and Symptoms
The most notable symptom of keratosis pilaris is its appearance—small, rough bumps that resemble goosebumps or chicken skin. These bumps are often flesh-colored but can also appear red or white.
How to Identify Keratosis Pilaris at Different StagesI
n its early stages, keratosis pilaris may present as mild roughness on the skin. As it progresses, more noticeable bumps may form, sometimes accompanied by slight redness or irritation.
Distinguishing Keratosis Pilaris from Other Skin Conditions
Keratosis pilaris is often confused with acne due to its bumpy texture. However, unlike acne, these bumps are not inflamed or painful and do not contain pus.
Types of Keratosis Pilaris
Keratosis Pilaris Rubra: Red Bumps on the Skin
This type involves red bumps that are more pronounced due to inflammation around the hair follicles.
Keratosis Pilaris Alba: White Bumps and Dry Skin
Characterized by white bumps without surrounding redness, this type is often associated with dry skin.
Seasonal Variations: Summer vs. Winter Symptoms
Symptoms tend to worsen in winter due to lower humidity levels and improve in summer when moisture levels are higher.
Keratosis Pilaris on Different Body Parts
Keratosis Pilaris on Arms
The upper arms are one of the most common areas affected by keratosis pilaris due to their higher density of hair follicles.
Keratosis Pilaris on Legs
Bumps on the thighs are also common and can extend down to the calves in some cases.
Facial Keratosis Pilaris
While less common, keratosis pilaris can appear on the face, particularly on the cheeks and around the eyes.
Keratosis Pilaris on Buttocks
This area can also be affected, often presenting as rough patches rather than distinct bumps.
Who is Affected by Keratosis Pilaris?
Genetic Predisposition and Family History
Keratosis pilaris often has a genetic component, meaning it can run in families. If one or both parents have the condition, their children are more likely to develop it as well.
This hereditary aspect suggests that certain genetic factors may predispose individuals to keratin buildup in hair follicles.
Keratosis Pilaris in Children vs. Adults
Children: Keratosis pilaris is particularly common in children and adolescents. The condition often appears during childhood and may worsen during puberty due to hormonal changes.
In many cases, the symptoms improve or even disappear as the child grows older.
Adults: While keratosis pilaris can persist into adulthood, it often becomes less noticeable with age.
Some adults continue to experience symptoms, especially if they have dry skin or other related skin conditions.
The Prevalence in Different Age Groups and Ethnicities
Keratosis pilaris affects people of all ages and ethnicities, though it is more commonly observed in children and teenagers. Certain ethnic groups may experience varying degrees of severity, but the condition is widespread across different populations.

Diagnosis of Keratosis Pilaris
How Dermatologists Diagnose Keratosis Pilaris
Dermatologists typically diagnose keratosis pilaris through a simple visual examination of the skin. The characteristic appearance of rough, bumpy skin is usually sufficient for diagnosis. In rare cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to rule out other conditions.
Can You Self-Diagnose Keratosis Pilaris?
While self-diagnosis is possible due to the distinct appearance of keratosis pilaris, consulting a dermatologist is recommended for an accurate diagnosis. This is particularly important if you are experiencing severe symptoms or if the condition is affecting your quality of life.
The Importance of Professional Diagnosis for Severe Cases
In severe cases, professional diagnosis is crucial to rule out other skin conditions that may require different treatment approaches. A dermatologist can also provide guidance on effective treatment options tailored to your specific needs.
Treatment Options for Keratosis Pilaris
Over-the-Counter Treatments: Creams, Lotions, and Exfoliants
Several over-the-counter products can help manage keratosis pilaris:
- Moisturizing Creams: Regular use of moisturizing creams can help soften the skin and reduce the appearance of bumps.
- Exfoliating Lotions: Products containing alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) can help exfoliate dead skin cells and improve skin texture.
- Urea Creams: Urea-based creams help dissolve the keratin plugs and hydrate the skin.
Prescription Treatments for Severe Keratosis Pilaris
For more severe cases, dermatologists may prescribe stronger treatments:
- Topical Retinoids: These vitamin A derivatives help increase cell turnover and prevent hair follicle blockage.
- Steroid Creams: In cases of inflammation or redness, steroid creams may be prescribed to reduce symptoms.
The Role of Chemical Exfoliation in Managing Symptoms
Chemical exfoliants like salicylic acid and lactic acid play a significant role in managing keratosis pilaris by dissolving dead skin cells and unclogging pores. Regular use can lead to smoother skin texture over time.
Moisturizers for Keratosis Pilaris
Best Moisturizers to Soothe Dry Skin
Moisturizing is a crucial step in managing keratosis pilaris, as it helps to soften the rough bumps and alleviate dryness. Look for moisturizers that contain:
- Glycerin: A humectant that draws moisture into the skin.
- Ceramides: Lipid molecules that help restore the skin barrier.
- Urea: Softens and hydrates the skin while dissolving keratin plugs.
How to Incorporate Moisturizers into Your Skincare Routine
- Daily Application: Apply moisturizer at least twice a day, especially after bathing when the skin is still damp.
- Gentle Massage: Use gentle circular motions to massage the moisturizer into the affected areas, ensuring even coverage.
- Consistency: Regular application is key to maintaining skin hydration and minimizing symptoms.
The Role of Humectants, Emollients, and Occlusives
- Humectants: Ingredients like glycerin and hyaluronic acid attract water to the skin, keeping it hydrated.
- Emollients: Such as shea butter and squalane, smooth and soften the skin by filling in gaps between skin cells.
- Occlusives: Ingredients like petrolatum create a barrier on the skin’s surface to lock in moisture.
Exfoliation for Keratosis Pilaris
Physical vs. Chemical Exfoliation: Which is Best?
- Physical Exfoliation: Involves using scrubs or brushes to manually remove dead skin cells. While effective, it can be too harsh for sensitive skin if not done gently.
- Chemical Exfoliation: Utilizes acids like salicylic acid or lactic acid to dissolve dead skin cells without abrasive action. This method is often preferred for its gentler approach.
Safe Exfoliation Practices to Prevent Skin Irritation
- Frequency: Limit exfoliation to 2-3 times per week to avoid over-exfoliating and irritating the skin.
- Gentle Products: Choose products specifically formulated for sensitive or keratosis pilaris-prone skin.
- Patch Test: Always perform a patch test before using new exfoliating products.
The Role of Salicylic Acid, Lactic Acid, and Urea
- Salicylic Acid: A beta hydroxy acid (BHA) that penetrates deep into pores to dissolve dead skin cells and unclog hair follicles.
- Lactic Acid: An alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) that gently exfoliates the surface of the skin while providing hydration.
- Urea: Helps break down keratin buildup while moisturizing the skin.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies for Keratosis Pilaris
Dietary Changes That May Improve Skin Health
While there is no specific diet for keratosis pilaris, maintaining a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins A, C, and E can support overall skin health. Foods such as fish, nuts, seeds, and leafy greens are beneficial.
Hydration and Its Impact on Skin Texture
Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water helps maintain skin elasticity and hydration from within, potentially reducing the severity of keratosis pilaris symptoms.
The Importance of Managing Humidity and Climate
Dry air can exacerbate keratosis pilaris symptoms. Using a humidifier in your home can help maintain optimal humidity levels, preventing excessive dryness that worsens the condition.
Can Keratosis Pilaris Be Cured?
Managing Expectations: Is There a Cure?
Keratosis pilaris is a chronic skin condition with no known cure. However, it can be managed effectively with consistent skincare routines and lifestyle adjustments. The goal is to minimize symptoms and improve the skin’s appearance over time.
Long-Term Management Tips for Flare-Ups
- Consistent Skincare: Maintain a regular regimen of moisturizing and gentle exfoliation to keep the skin smooth.
- Avoid Harsh Products: Steer clear of products that can irritate the skin, such as harsh soaps or alcohol-based lotions.
- Monitor Triggers: Identify and avoid environmental factors that exacerbate symptoms, such as dry weather or hot showers.
How to Minimize the Appearance of Bumps Over Time
- Regular Exfoliation: Use chemical exfoliants like salicylic acid or lactic acid to gently remove dead skin cells.
- Hydration: Keep the skin well-moisturized to prevent dryness and roughness.
- Sun Protection: Use sunscreen to protect the skin from UV damage, which can worsen keratosis pilaris.
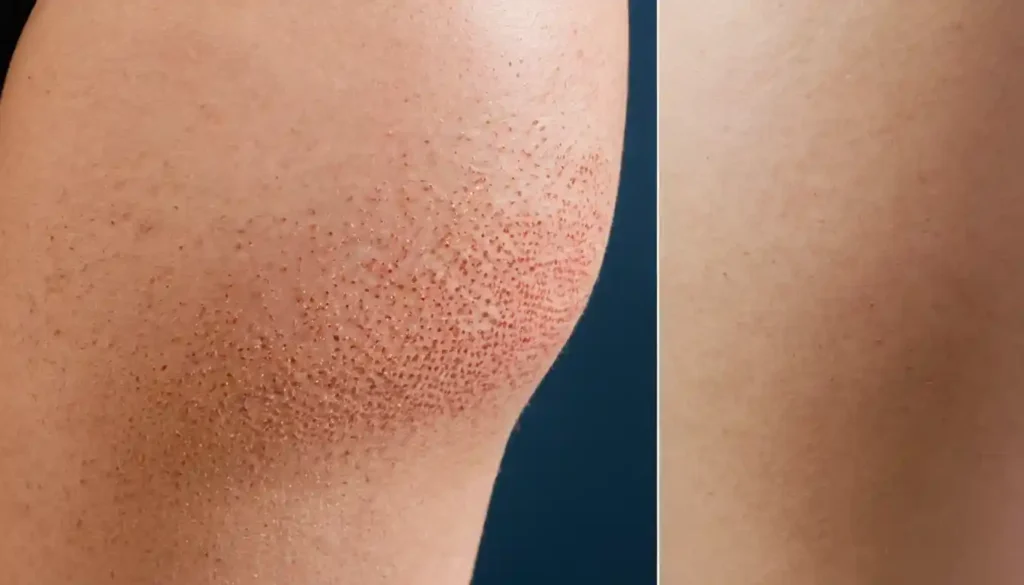
Natural Remedies for Keratosis Pilaris
Coconut Oil, Aloe Vera, and Other Natural Solutions
- Coconut Oil: Known for its moisturizing properties, coconut oil can help soften the skin and reduce roughness.
- Aloe Vera: Soothes irritation and provides hydration, making it a gentle option for sensitive skin.
- Oatmeal Baths: Adding colloidal oatmeal to baths can relieve itching and smooth the skin.
Popular Home Remedies for Softening the Skin
- Baking Soda Scrub: A mild exfoliant that can help slough off dead skin cells when used gently.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Diluted apple cider vinegar may help balance the skin’s pH and reduce bumps.
- Honey Masks: Honey’s natural humectant properties can hydrate and soften the skin.
The Effectiveness of Natural Exfoliants
Natural exfoliants like sugar or ground coffee can be used as gentle scrubs. However, they should be used with caution to avoid irritating sensitive areas affected by keratosis pilaris.
Keratosis Pilaris and Mental Health
How Keratosis Pilaris Affects Self-Esteem
The visible nature of keratosis pilaris can impact self-esteem, especially in social situations where exposed skin is involved. Many individuals feel self-conscious about their appearance due to the condition’s persistent nature.
Coping Strategies for Skin-Related Anxiety and Insecurities
- Education: Understanding that keratosis pilaris is common and harmless can alleviate some anxiety.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide emotional support.
- Professional Help: Consulting a dermatologist or therapist can offer both medical advice and psychological support.
Prevention Tips for Keratosis Pilaris
Preventing Flare-Ups During Seasonal Changes
Keratosis pilaris symptoms often fluctuate with the seasons, worsening in colder months due to dry air. Here are some tips to manage flare-ups:
- Use a Humidifier: Maintain indoor humidity to prevent skin from drying out.
- Avoid Hot Showers: Opt for lukewarm water to prevent stripping natural oils from the skin.
- Moisturize Regularly: Apply a thick, emollient-rich moisturizer immediately after bathing.
Best Practices for Reducing Dry Skin and Bumps
- Gentle Cleansing: Use mild, fragrance-free cleansers to avoid irritating the skin.
- Regular Exfoliation: Incorporate gentle exfoliation into your routine to remove dead skin cells and prevent buildup.
- Protective Clothing: Wear breathable fabrics to minimize irritation and friction on affected areas.
How to Protect Skin During Winter Months
- Layering Skincare Products: Use a combination of humectants, emollients, and occlusives to lock in moisture.
- Sunscreen: Even in winter, UV rays can affect the skin. Apply sunscreen daily to protect against damage.
- Hydration: Increase water intake to help maintain skin hydration from within.
Frequently Asked Questions about Keratosis Pilaris
Is Keratosis Pilaris Contagious?
No, keratosis pilaris is not contagious. It is a genetic condition that cannot be spread through contact.
Can Keratosis Pilaris Go Away on Its Own?
In many cases, keratosis pilaris improves with age and may even disappear over time. However, consistent skincare can help manage symptoms more effectively.
Will Scrubbing Make Keratosis Pilaris Worse?
Aggressive scrubbing can irritate the skin and worsen keratosis pilaris. It’s best to use gentle exfoliation methods to avoid exacerbating the condition.
What Is the Best Treatment for Children with Keratosis Pilaris?
For children, mild moisturizers and gentle exfoliants are recommended. Always consult a pediatric dermatologist before introducing new treatments.
Can Keratosis Pilaris Worsen Over Time?
While keratosis pilaris doesn’t typically worsen over time, it can become more noticeable during periods of dry weather or if not managed properly.
Keratosis Pilaris in Children
Managing Keratosis Pilaris in Infants and Toddlers
In young children, focus on gentle skincare routines:
- Use mild cleansers and moisturizers designed for sensitive skin.
- Avoid harsh soaps and lotions that may irritate their delicate skin.
Explaining the Condition to Children
Help children understand that keratosis pilaris is a common and harmless condition. Encourage them not to scratch or pick at their skin to prevent irritation.
Safe Treatments for Young Skin
Opt for products specifically formulated for children’s sensitive skin. Consult with a pediatric dermatologist for personalized recommendations.
Best Products for Keratosis Pilaris
Top-Rated Creams for Treating Keratosis Pilaris
- AmLactin Daily Moisturizing Body Lotion: Contains lactic acid to gently exfoliate and hydrate the skin, improving texture over time.
- CeraVe SA Lotion for Rough & Bumpy Skin: Features salicylic acid and ceramides to exfoliate and restore the skin barrier.
- Eucerin Roughness Relief Lotion: Combines urea and ceramides to soften rough patches and enhance moisture retention.
Effective Exfoliating Tools for Rough Skin
- Exfoliating Gloves: Provide gentle manual exfoliation to remove dead skin cells without causing irritation.
- Soft-Bristled Brushes: Ideal for sensitive areas, helping to smooth skin texture when used in moderation.
Sunscreens That Won’t Worsen Keratosis Pilaris
- La Roche-Posay Anthelios Melt-in Milk Sunscreen: Offers broad-spectrum protection without clogging pores or irritating the skin.
- Neutrogena Sheer Zinc Dry-Touch Sunscreen: A mineral-based sunscreen that is gentle on sensitive skin and suitable for daily use.
The Role of Climate in Keratosis Pilaris
How Weather Affects Skin Condition
Weather changes can significantly impact keratosis pilaris symptoms:
- Cold, Dry Climates: Often exacerbate dryness and roughness, leading to more pronounced symptoms.
- Warm, Humid Climates: Tend to improve skin hydration naturally, reducing the severity of keratosis pilaris.
Seasonal Changes and Adjustments to Your Skincare Routine
- Winter Adjustments:
- Increase moisturizing frequency and use richer creams.
- Incorporate humidifiers indoors to maintain skin hydration.
- Summer Adjustments:
- Use lighter lotions to prevent excess oiliness.
- Continue sun protection to prevent UV damage.
Conclusion
Living with Keratosis Pilaris: Effective Management Strategies
Managing keratosis pilaris involves a combination of consistent skincare routines, lifestyle adjustments, and understanding individual triggers. By implementing these strategies, individuals can significantly reduce the appearance of bumps and improve overall skin texture.
Embracing Long-Term Skin Care for Healthier Skin
While keratosis pilaris may not have a cure, its symptoms can be effectively managed with dedication to skincare practices. Embracing a routine that includes regular moisturizing, gentle exfoliation, and protection against environmental factors will lead to healthier skin over time.







