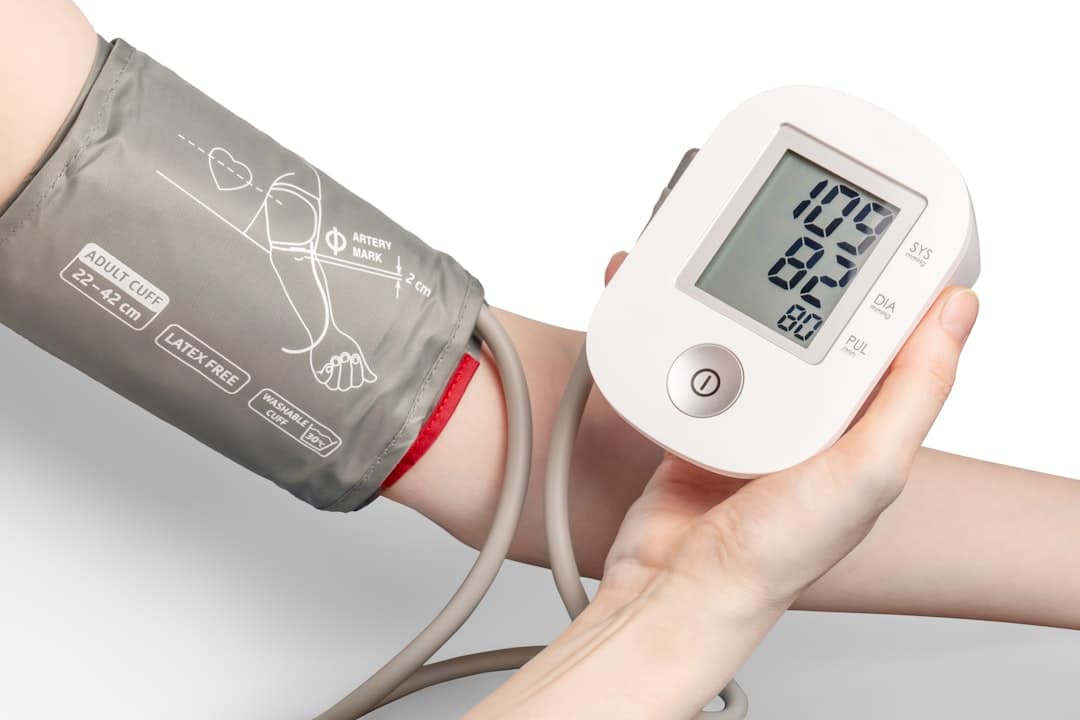
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a chronic medical condition characterized by elevated pressure in the arteries, which can lead to serious health complications if left unmanaged. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is expressed with two numbers: systolic pressure (the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats) over diastolic pressure (the pressure in the arteries when the heart rests between beats). A normal reading is typically around 120/80 mmHg, while hypertension is generally defined as having a reading of 130/80 mmHg or higher.
The condition often develops over many years and can go unnoticed, earning it the moniker “the silent killer.” The causes of high blood pressure are multifaceted and can include genetic predisposition, poor dietary habits, lack of physical activity, obesity, and chronic stress. Additionally, certain medical conditions such as diabetes and kidney disease can contribute to the development of hypertension. Understanding these underlying factors is crucial for effective management and prevention.
The implications of untreated high blood pressure are severe; it can lead to heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and other life-threatening conditions. Therefore, recognizing the signs and risk factors associated with hypertension is essential for early intervention and treatment.
Key Takeaways
- High blood pressure is a common condition that can lead to serious health issues if left untreated.
- Making lifestyle changes such as exercising regularly and managing stress can help lower blood pressure.
- Dietary modifications, including reducing sodium intake and increasing potassium-rich foods, can also help manage high blood pressure.
- Regular exercise is important for managing high blood pressure and overall cardiovascular health.
- Stress management techniques such as meditation and deep breathing can help lower blood pressure and improve overall well-being.
Lifestyle Changes for Lowering Blood Pressure
Adopting a Balanced Diet
One of the primary lifestyle modifications involves adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while minimizing processed foods high in sodium and unhealthy fats. The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet is frequently recommended for individuals with hypertension, emphasizing nutrient-dense foods that can help lower blood pressure.
Incorporating Regular Physical Activity
In addition to dietary changes, incorporating regular physical activity into daily routines is vital. Engaging in aerobic exercises such as walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming for at least 150 minutes per week can help lower blood pressure and improve heart health.
Reducing Sedentary Behavior
Furthermore, reducing sedentary behavior by standing or moving around during long periods of inactivity can also contribute positively to blood pressure management. These lifestyle changes not only help in controlling hypertension but also enhance overall well-being and quality of life.
Dietary Modifications for Managing High Blood Pressure

Diet plays a pivotal role in managing high blood pressure. One of the most significant dietary modifications involves reducing sodium intake.
The American Heart Association recommends limiting sodium consumption to no more than 2,300 mg per day, with an ideal limit of 1,500 mg for those with hypertension.
High sodium levels can cause the body to retain water, leading to increased blood volume and higher blood pressure. Reading food labels and choosing low-sodium options can be effective strategies for managing sodium intake.
Incorporating potassium-rich foods into the diet is another beneficial modification. Potassium helps balance sodium levels in the body and can mitigate its hypertensive effects. Foods such as bananas, oranges, spinach, sweet potatoes, and beans are excellent sources of potassium.
Additionally, increasing fiber intake through whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can support heart health by improving cholesterol levels and promoting healthy digestion. By focusing on a diet that emphasizes whole foods while minimizing processed options, individuals can create a sustainable eating pattern that supports long-term blood pressure management.
The Importance of Regular Exercise
| Benefits of Regular Exercise | Statistics |
|---|---|
| Improves overall health | 80% of adults do not meet the guidelines for both aerobic and muscle-strengthening activities |
| Reduces the risk of chronic diseases | 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week can reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases |
| Enhances mental well-being | Regular physical activity can reduce the risk of depression and anxiety |
| Improves sleep quality | People who exercise regularly are more likely to have better sleep quality |
| Increases longevity | Regular exercise can increase life expectancy by up to 7 years |
Regular exercise is a cornerstone of effective hypertension management. Engaging in physical activity not only helps lower blood pressure but also strengthens the heart muscle, improves circulation, and enhances overall cardiovascular health. Aerobic exercises such as brisk walking, running, cycling, or swimming are particularly beneficial for individuals with high blood pressure.
These activities increase heart rate and promote better blood flow throughout the body. Moreover, strength training exercises can also play a role in managing hypertension. Incorporating resistance training into a fitness routine at least two days a week can help build muscle mass and improve metabolic health.
Studies have shown that consistent exercise can lead to reductions in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure readings. It is essential for individuals to find activities they enjoy to maintain motivation and consistency in their exercise routines. Even small changes, such as taking the stairs instead of the elevator or engaging in active hobbies like gardening or dancing, can contribute positively to blood pressure management.
Stress Management Techniques
Chronic stress is a significant contributor to high blood pressure and can exacerbate existing hypertension. Therefore, implementing effective stress management techniques is crucial for individuals seeking to lower their blood pressure levels. Mindfulness practices such as meditation and deep breathing exercises have been shown to reduce stress and promote relaxation.
These techniques help activate the body’s relaxation response, which can lower heart rate and blood pressure. Additionally, engaging in activities that promote mental well-being—such as yoga, tai chi, or even simple hobbies like painting or gardening—can provide an outlet for stress relief.
Social support also plays a vital role in managing stress; spending time with friends and family or participating in community activities can foster a sense of belonging and reduce feelings of isolation.
By prioritizing mental health and incorporating stress-reducing practices into daily life, individuals can create a more balanced lifestyle that supports healthy blood pressure levels.
Medication Options for High Blood Pressure
Types of Antihypertensive Medications
There are several classes of medications available, each working through different mechanisms to lower blood pressure. Common categories include diuretics, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), calcium channel blockers, and beta-blockers.
How Medications Work
Diuretics help the body eliminate excess sodium and water through urine, reducing blood volume and lowering blood pressure. ACE inhibitors work by blocking the formation of angiotensin II—a hormone that constricts blood vessels—thereby promoting vasodilation and lowering blood pressure. ARBs serve a similar purpose by blocking the action of angiotensin II at its receptor sites. Calcium channel blockers prevent calcium from entering heart and blood vessel cells, leading to relaxed blood vessels and reduced heart workload. Beta-blockers decrease heart rate and cardiac output, which can also contribute to lower blood pressure levels.
Importance of Patient-Provider Collaboration
It is essential for patients to work closely with their healthcare providers to determine the most appropriate medication regimen based on their individual health needs.
Monitoring and Tracking Blood Pressure Levels
Regular monitoring of blood pressure levels is crucial for effective management of hypertension. Individuals diagnosed with high blood pressure should regularly check their readings at home using a reliable digital sphygmomanometer or visit their healthcare provider for routine assessments. Keeping a log of these readings can help identify patterns or fluctuations over time and provide valuable information for healthcare professionals when adjusting treatment plans.
Home monitoring allows individuals to take an active role in their health management by providing immediate feedback on how lifestyle changes or medications are affecting their blood pressure levels. It also helps raise awareness about the importance of maintaining healthy habits consistently. Patients should be educated on how to measure their blood pressure correctly—such as sitting quietly for a few minutes before taking a reading and ensuring proper cuff placement—to ensure accuracy in their measurements.
The Role of Weight Management in Lowering Blood Pressure
Weight management is another critical factor in controlling high blood pressure. Excess body weight places additional strain on the heart and increases the risk of developing hypertension. Studies have shown that even modest weight loss—around 5-10% of total body weight—can lead to significant reductions in blood pressure levels for overweight or obese individuals.
This reduction occurs due to improved insulin sensitivity, decreased inflammation, and enhanced cardiovascular function associated with weight loss. To achieve sustainable weight loss, individuals should focus on creating a caloric deficit through a combination of dietary modifications and increased physical activity. Setting realistic goals and making gradual changes can lead to long-term success rather than quick fixes that may not be maintainable over time.
Additionally, seeking support from healthcare professionals or registered dietitians can provide personalized guidance tailored to individual needs and preferences.
Limiting Alcohol and Caffeine Intake
Both alcohol and caffeine consumption can influence blood pressure levels; therefore, moderation is key for individuals managing hypertension. Excessive alcohol intake has been linked to elevated blood pressure readings; thus, it is recommended that men limit their consumption to no more than two drinks per day while women should limit it to one drink per day. Reducing alcohol intake not only helps lower blood pressure but also contributes to overall health improvements.
Caffeine’s effects on blood pressure are more complex; while some studies suggest that caffeine may cause temporary spikes in blood pressure, others indicate that habitual coffee drinkers may develop a tolerance over time. Nonetheless, it is advisable for individuals with hypertension to monitor their caffeine intake from sources such as coffee, tea, energy drinks, and certain medications containing caffeine. Gradually reducing caffeine consumption may be beneficial for those who are sensitive to its effects.
Seeking Support and Guidance from Healthcare Professionals
Navigating the complexities of managing high blood pressure can be challenging; therefore, seeking support from healthcare professionals is essential for effective treatment and guidance. Primary care physicians play a crucial role in diagnosing hypertension and developing personalized treatment plans that may include lifestyle modifications, medication management, or referrals to specialists such as cardiologists or dietitians. Regular check-ups allow healthcare providers to monitor progress over time and make necessary adjustments based on individual responses to treatment strategies.
Additionally, educational resources provided by healthcare professionals can empower patients with knowledge about their condition and encourage proactive engagement in their health management journey.
Creating a Holistic Approach to Managing High Blood Pressure
Managing high blood pressure effectively requires a holistic approach that encompasses various aspects of health—physical activity, nutrition, stress management, medication adherence, and regular monitoring—all working synergistically toward achieving optimal outcomes. By integrating these elements into daily life, individuals can create a comprehensive strategy that addresses both the symptoms and underlying causes of hypertension. This holistic approach emphasizes the importance of viewing health as an interconnected system rather than isolated components; for instance, recognizing how stress impacts dietary choices or how physical activity influences mental well-being can lead to more informed decision-making regarding lifestyle changes.
Ultimately, fostering a supportive environment—whether through community resources or personal relationships—can enhance motivation and accountability in managing high blood pressure effectively over time.
If you are looking for ways to manage high blood pressure, one important step is to maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise. In addition, it is crucial to monitor your blood pressure regularly and follow your doctor’s recommendations for medication and lifestyle changes. For more information on how to improve your overall health, you can check out this article on Musely Skin Care Reviews: Honest Consumer Feedback 2023. This article provides valuable insights into skincare products that can help you look and feel your best.
FAQs
What is considered high blood pressure?
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is when the force of blood against the walls of your arteries is consistently too high. It is typically defined as a reading of 130/80 mmHg or higher.
What are the potential risks of high blood pressure?
High blood pressure can lead to serious health issues such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and other complications. It is important to manage and control high blood pressure to reduce these risks.
What lifestyle changes can help lower high blood pressure?
Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, limiting alcohol consumption, reducing sodium intake, and managing stress can help lower high blood pressure.
When should I seek medical attention for high blood pressure?
If you have consistently high blood pressure readings, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. They can provide guidance on treatment options and help monitor your blood pressure to prevent potential health complications.
What are the treatment options for high blood pressure?
Treatment options for high blood pressure may include medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. It is important to work with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for managing high blood pressure.