Table of Contents
Melanoma is a serious type of skin cancer that can be life-threatening if not detected early. Understanding melanoma, its symptoms, and prevention methods is crucial for everyone, especially those at higher risk. This article will explain what melanoma is, how to recognize it, and what steps you can take to protect yourself.
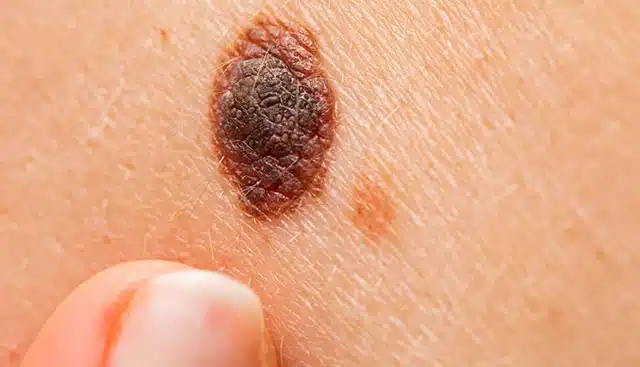
What is Melanoma?
Melanoma is a type of cancer that begins in the melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin, which gives skin its color. While melanoma is less common than other types of skin cancer, it is the most dangerous because it can spread to other parts of the body if not treated early.Melanoma can appear anywhere on the body, including areas not usually exposed to the sun, such as the soles of the feet, palms of the hands, and even under the nails. It can also develop in existing moles or appear as new spots on the skin.
Who is at Risk?
Anyone can develop melanoma, but certain factors can increase your risk:
- Fair Skin: People with light skin, freckles, or red or blonde hair are at a higher risk.
- Sun Exposure: Spending a lot of time in the sun or using tanning beds increases the risk of melanoma.
- Family History: If someone in your family has had melanoma, your risk may be higher.
- Moles: Having many moles or unusual moles can increase the risk of developing melanoma.
- Weakened Immune System: People with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy, are at greater risk.
Recognizing Melanoma: The ABCDEs
One of the best ways to detect melanoma early is to know the signs. Dermatologists often use the ABCDE method to help people remember what to look for in moles or spots on the skin:
- A for Asymmetry: If you draw a line through the mole, the two halves do not match. Non-cancerous moles are usually symmetrical.
- B for Border: Melanomas often have irregular, notched, or scalloped edges. Benign moles typically have smooth, even borders.
- C for Color: Melanomas can be multiple colors, including brown, black, tan, red, white, or blue. Benign moles are usually a single shade.
- D for Diameter: Melanomas are often larger than 6mm (about the size of a pencil eraser). However, they can be smaller when first detected.
- E for Evolving: Any change in size, shape, color, or elevation of a mole, or any new symptom such as bleeding, itching, or crusting, is a warning sign.
If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Prevention Tips
Preventing melanoma involves protecting your skin from harmful UV rays and being vigilant about skin checks. Here are some effective prevention strategies:
1. Use Sunscreen
Applying sunscreen is one of the most important steps you can take to protect your skin. Choose a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. Apply it generously to all exposed skin, even on cloudy days. Reapply every two hours, or more often if swimming or sweating.
2. Wear Protective Clothing
When outdoors, wear protective clothing such as long sleeves, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses. Look for clothes made from UV-protective fabric for added protection.
3. Seek Shade
Avoid direct sunlight, especially during peak hours between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. When possible, seek shade under trees, umbrellas, or canopies.
4. Avoid Tanning Beds
Tanning beds expose your skin to harmful UV radiation, increasing your risk of developing melanoma. It’s best to avoid them altogether.
5. Regular Skin Checks
Perform regular self-examinations of your skin to check for any new or changing moles. Look for spots that fit the ABCDE criteria. It’s also a good idea to have a dermatologist perform a full skin examination at least once a year, especially if you are at higher risk.
What to Do If You Find a Suspicious Mole
If you notice a mole that has changed or a new spot that looks concerning, don’t panic. Most skin lesions are not cancerous, but it’s essential to get them checked out. Here’s what to do:
- Make an Appointment: Schedule an appointment with a dermatologist. They can examine your skin and determine if further testing is needed.
- Bring a List: If you have multiple moles or spots, consider bringing a list or photos to help your doctor assess any changes over time.
- Follow Up: If your doctor recommends a biopsy or further testing, be sure to follow through. Early detection is key to successful treatment.
Treatment Options for Melanoma
If diagnosed with melanoma, the treatment will depend on the stage of the cancer. Here are some common treatment options:
- Surgery: The most common treatment for melanoma is surgical removal of the cancerous tissue. This may involve removing the melanoma itself and some surrounding healthy skin.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment helps your immune system fight cancer. It may be used for advanced melanoma.
- Targeted Therapy: This type of treatment targets specific mutations in cancer cells. It’s often used for melanoma with certain genetic changes.
- Chemotherapy: In some cases, chemotherapy may be used to kill cancer cells, especially if the melanoma has spread.
- Radiation Therapy: This treatment uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. It’s not commonly used for melanoma but may be helpful in some cases.
Conclusion
Melanoma is a serious skin cancer that can be life-threatening if not caught early. By understanding what melanoma is, recognizing the signs, and taking preventive measures, you can protect yourself and your skin. Regular skin checks and sun protection are key to reducing your risk. If you notice any changes in your skin, don’t hesitate to see a doctor. Early detection can lead to successful treatment and a better outcome. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and take care of your skin!
Read More :
What are the early symptoms of melanoma ?
What are the common pitfalls when choosing skincare products ?
How can I tell if a skincare product is truly effective ?
What are the most common skincare myths that dermatologists encounter ?
What Dermatologists Want You to Know About Skincare Myths ?
